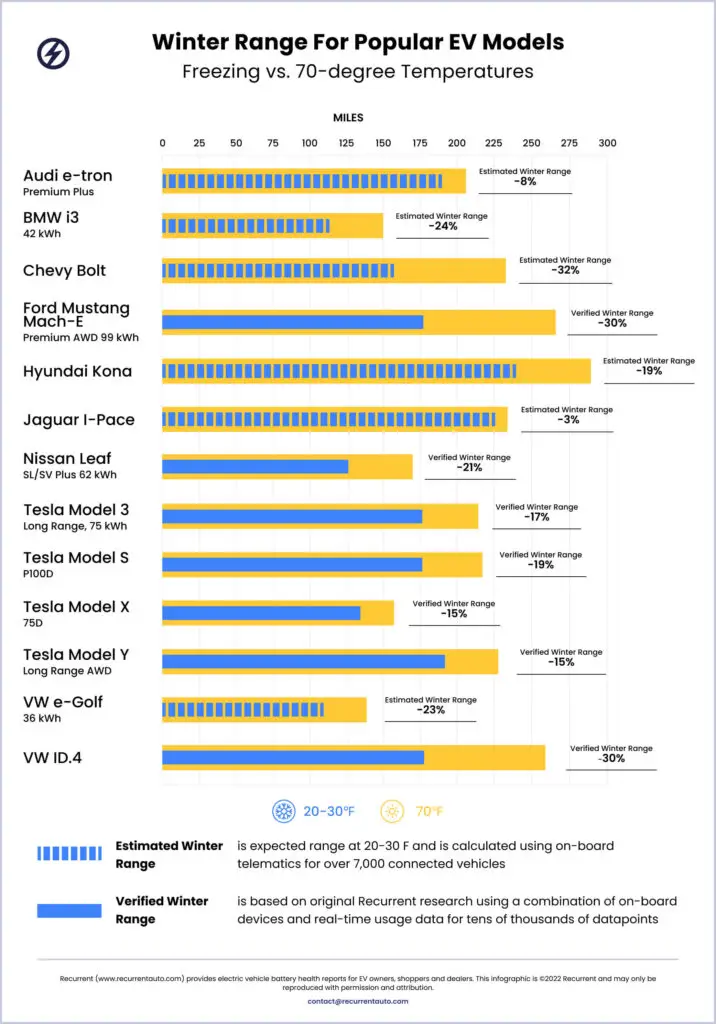
As technology continues to advance, it’s becoming increasingly clear that the performance of electronic devices can be greatly impacted by changes in temperature. This is especially true for electric vehicles (EVs), which rely heavily on the functionality of their batteries. According to an expert at RecurrentAuto.com, some EVs can experience a loss of up to 160 kilometres or 35% of their range in cold temperatures.
There are a few reasons for this decrease in performance. An important factor to consider is the fact that EVs require more energy to heat themselves than traditional internal combustion engines. This is because internal combustion engines are able to produce a significant amount of heat that is typically wasted during the summer months, but can be redirected to warm the cabin during the winter. On the other hand, EVs are much more efficient, so the small amount of heat that is generated by the motor is primarily used to warm the battery.
Another major factor is the physical and chemical reactions that occur within the battery itself, which can slow down significantly in colder temperatures. While all cars lose efficiency in cold weather, this reduction in power can be attributed to the fact that the cold temperatures disrupt the usual chemical reactions that occur within the battery, resulting in lowered energy output.
It’s worth noting that lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in most EVs, are also affected by higher temperatures. In fact, these types of batteries tend to degrade more quickly when exposed to warm temperatures. This is because the rate of chemical reactions inside the battery is directly influenced by temperature, so the higher the temperature, the faster the reactions occur, which results in more energy being produced, but also faster degradation of the battery. However, this is where heat pumps come into play.
What is a heat pump?
A heat pump in an electric vehicle (EV) is a device that uses a small amount of electrical energy to move heat from one place to another. In an EV, it is used to heat the passenger compartment and the battery, which helps to increase the range of the vehicle in cold weather. Heat pumps are becoming more and more commonplace in new EV models, while aftermarket options are available to retrofit older models. These heat pumps are more efficient than traditional resistance heaters because they use less energy to produce the same amount of heat. They are also more environmentally friendly because they do not produce emissions like traditional combustion-based heaters do. It’s worth noting that heat pumps can be expensive and may not be worth the added range they can provide.
Planning for the cold weather
Pre-planning is always the best way to prepare for potential effects from cold weather. Factoring in your car’s potential range loss is a great way to do this. RecurrentAuto recently published a study showing the cold weather changes in range for some of the most popular EVs in the market today.
If you are thinking about purchasing a used EV, we highly recommend using EVFriendly’s Inspection Guidebook and Inspection Checklist. These are free, comprehensive resources to help consumers stay informed and make the most of their used EV purchase. We highly recommend using a qualified EV technician.
Conclusion
With the Canadian government’s new regulations mandating that a significant proportion (⅕) of all passenger cars, SUVs, and trucks sold in Canada must run on electricity by 2026 and 100% of cars by 2035, it’s becoming increasingly important for Canadians to have a better understanding of how EVs perform in different temperatures and how to plan around it.